
What Does Switzerland Export To The US? A Detailed Guide
Switzerland plays a vital role in U.S. trade, supplying a wide range of high-value and specialized products. From pharmaceuticals and


In the vast world of international commerce, a small but powerful classification system plays a critical role in cross-border trade: the Harmonized Tariff Schedule, commonly known as the HTS code.
While it may look like a simple string of numbers, an HTS code is a country-specific extension of the global Harmonized System (HS), which is maintained by the World Customs Organization.
Customs authorities, importers, and exporters rely on these codes to classify goods, determine duty rates, and ensure regulatory compliance. In the United States, this system is formally known as the HTSUS and is essential for all import transactions.
Whether you are an experienced global trader or new to importing and exporting, understanding HTS codes is a foundational step in managing customs requirements and avoiding costly errors.
As trade regulations continue to evolve, accurate classification remains a key part of compliant and efficient supply chains. Artemus Transportation Solutions supports businesses with ISF filing, AMS & AES compliance, customs broker software solutions, and related trade compliance services.
Table Of Contents
The HTS Code, or Harmonized Tariff Schedule code, is a standardized numerical system used to classify imported goods for customs purposes in the United States. It is based on the global Harmonized System developed by the World Customs Organization and provides a common framework for product classification worldwide.
In the US, the Harmonized System (HS) is extended to a 10-digit HTS code. These additional digits are used to determine applicable import duties, taxes, and any specific regulatory requirements tied to a product.
Each HTS code describes a product based on its material, function, and level of processing. Accurate HTS classification is critical for customs compliance, correct duty calculation, and avoiding shipment delays, audits, or financial penalties.

Related: How To Find A Customs Broker? 7 Important Factors To Know
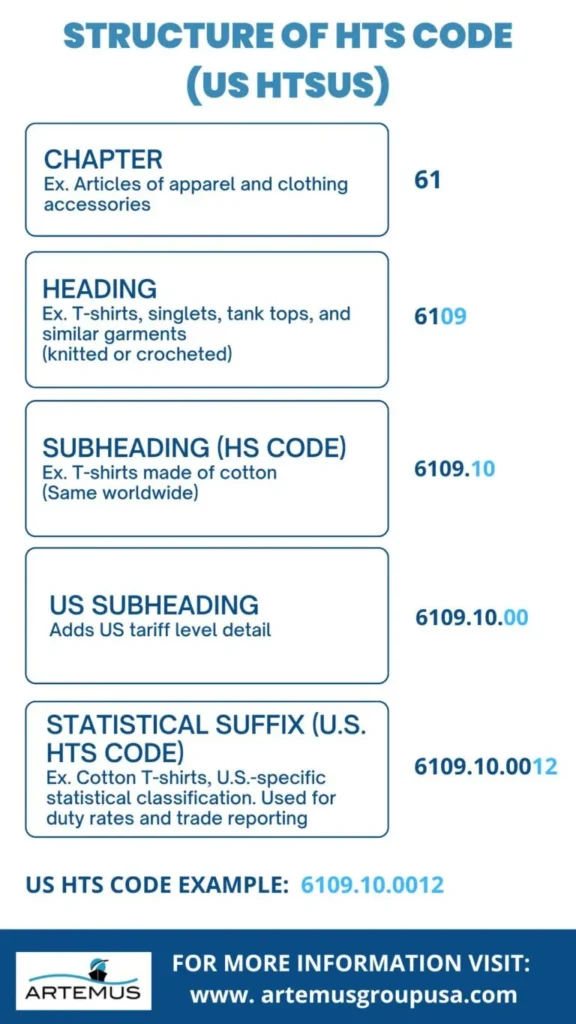
The structure of an HTS code follows a standardized 10 digit format used in the United States to classify imported goods. This system is formally known as the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTSUS).
While it is based on a global framework, HTS codes can vary by country, making accurate interpretation essential.
In the US, the HTS is administered by the US International Trade Commission, and product classification is determined by a product’s composition, form, and function.
Together, these six digits form the international HS code, also known as the Schedule B number, and remain consistent worldwide.
Example: US HTS code 6109.10.0012 (a cotton T-shirt)
The first four digits, 6109, represent the HS heading under Chapter 61, identifying T-shirts, singlets, and similar garments that are knitted or crocheted.
The next two digits form the subheading 6109.10, which classifies the product specifically as a cotton T-shirt, distinguishing it from garments made of synthetic or other fibers.
The final four digits, 0012, are U.S.-specific statistical suffixes used by U.S. Customs and Border Protection. These digits further refine the classification for trade statistics and duty assessment, often distinguishing factors such as gender or specific tariff categories applicable under U.S. law.
All 10 digits together define the complete HTS classification used for imports into the United States.
61 – CHAPTER
6109 – HEADING
6109.10 – SUBHEADING (HS CODE)
6109.10.00 – U.S. SUBHEADING
6109.10.0012 – STATISTICAL SUFFIX (U.S. HTS CODE)
Related: What Does A Customs Broker Do? 10 Key Responsibilities
Identifying the correct HTS code means selecting a 10 digit classification that accurately reflects your product’s material, function, and intended use. Because this code determines duties and compliance requirements, the process should be handled methodically rather than by guesswork.
Related: Customs Broker VS Freight Forwarder: 5 Key Differences
Determining the correct HTS code can be challenging, especially when product details are misunderstood or overlooked. Errors in classification often lead to compliance risks, delays, and unexpected costs.
Common issues include:

Related: Customs Broker Exam Registration: In-Person & Remote CBLE
When an HTS code is incorrect, it can disrupt the entire import process and expose the importer to financial and compliance risks. Because HTS codes determine duty rates, regulatory controls, and trade agreement eligibility, errors are taken seriously by customs authorities.
At the port of entry, shipments may be held for inspection or review, leading to delays, storage charges, and demurrage fees.
US Customs and Border Protection can also reclassify the product, often applying a higher duty rate than originally declared. In addition, penalties and fines may be issued for incorrect filings, even when mistakes are unintentional.
From a financial and compliance standpoint, underpaid duties must be repaid with interest, while overpaid duties require time-consuming refund claims. Repeated or intentional misclassification can raise red flags and may be treated as fraud, particularly for goods subject to anti-dumping or countervailing duties.
Incorrect HTS codes can also invalidate eligibility for free trade agreements or preferential duty programs, resulting in higher overall import costs.
Related: How To Become A Customs Broker? A Step-By-Step Journey
HTS codes are fundamental to the customs process, providing a standardized system for identifying and classifying imported goods. Accurate classification enables customs authorities to apply the correct duties, taxes, and regulatory controls, while helping importers avoid delays, penalties, and compliance issues.

Related: ISF Fees (Import Security Filing): When & How To Pay?
Here’s a clear comparison of HTS Code, HS Code, and Schedule B, highlighting their key differences while reflecting current and accurate trade practices:
HTS Code (Harmonized Tariff Schedule): The HTS Code is used by the United States for import classification. It is built on the international HS framework and extends it to 10 digits under the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTSUS), allowing US Customs to apply precise duty rates, taxes, and regulatory controls.
HS Code (Harmonized System): The HS Code is a globally standardized product classification system developed by the World Customs Organization. It uses a six-digit structure to provide a uniform baseline for identifying goods in international trade.
Schedule B: Schedule B is the US classification system used specifically for export reporting. It aligns with the HS Code at the six-digit level and extends to 10 digits for detailed export data collection and trade statistics.
HTS Code: In the United States, the HS Code is expanded to 10 digits. The additional four digits define US specific duty rates, trade remedies, and regulatory requirements for imports.
HS Code: The international HS standard is limited to six digits and does not include country specific extensions.
Schedule B: Schedule B also uses a 10-digit format, but the extra digits are designed for export reporting and statistical tracking rather than duty assessment.
HTS Code: Used exclusively for imports into the United States. The extended digits support detailed US customs enforcement and tariff application.
HS Code: Used worldwide as the common classification language for traded goods, forming the foundation for national tariff schedules.
Schedule B: Used only for US exports and required for filing Electronic Export Information through the Automated Export System (AES).
HTS Code: Provides the highest level of import classification detail for the US market, supporting accurate duty calculation and compliance checks.
HS Code: Offers a broad, standardized classification suitable for global trade alignment.
Schedule B: Provides export-focused detail to support trade data accuracy and compliance with US export reporting requirements.
HTS Code: Administered by the US International Trade Commission and enforced by US Customs and Border Protection under US import laws.
HS Code: Maintained by the World Customs Organization and adopted by member countries to promote consistency in international trade.
Schedule B: Managed by the US Census Bureau and used for export control, reporting, and trade statistics purposes.
Together, these systems work in alignment to support accurate classification, compliance, and reporting across both US imports and exports.
Related: Can A Customs Broker Be The Importer Of Record Legally?
To find your HTS code, use the USITC HTS search tool, review official customs documentation, or consult a licensed customs broker, ensuring classification is based on your product’s material, function, and use.
The main purpose of the HTS is to classify imported goods into the United States so customs authorities can apply the correct duties, taxes, and regulatory requirements.
In the United States, HTS codes are provided by the U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC) and enforced by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP).
To convert an HTS code to an HS code, use only the first six digits of the HTS code, as these digits represent the international HS classification used worldwide.
No. While both use a 10 digit format and share the same first six digits, HTS numbers are used for US imports, while Schedule B numbers are used for US exports and serve different regulatory and reporting purposes.

In the intricate world of international trade, the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) code emerges as a silent yet powerful force. Through our exploration, we’ve uncovered its significance as the universal language of customs, guiding the way for businesses engaged in global transactions. The HTS code’s role in facilitating smooth cross-border trade, determining tariff rates, and ensuring compliance with regulations cannot be overstated.
As we conclude this journey into the alphabet of commerce, it becomes evident that understanding and accurately applying the HTS code is not just a necessity but a strategic advantage for businesses navigating the intricacies of the global marketplace. In the ever-evolving landscape of international trade, the HTS code remains a crucial key to unlocking seamless and efficient cross-border transactions.
Related: AMS Fee In Shipping: Overview & 5 Key Considerations


Switzerland plays a vital role in U.S. trade, supplying a wide range of high-value and specialized products. From pharmaceuticals and

In 2026, the US-Europe trade relationship continues to power global commerce, driven by exports of energy, advanced machinery, and pharmaceuticals

The economic partnership between the United States and Norway is a sophisticated and evolving pillar of transatlantic commerce. U.S. exports
Get In Touch
Artemus’ Software Solutions for ISF, AMS, Japan AFR, eManifest Canada, & Panama B2B filings.