
What Does The US Export To Switzerland? Trade Insights
International trade between the United States and Switzerland highlights the strong economic relationship between the two nations. With its highly


Japan’s trade system is central to its economy, with imports like raw materials and food supporting its industries and population. This robust import network allows Japan to remain self-sufficient in areas where resources are limited domestically.
Japan’s exports, notably in automobiles, electronics, and machinery, reflect its expertise in precision and quality. Major trading partners, including the U.S., China, and South Korea, rely heavily on Japanese goods, showcasing Japan’s influence in global markets.
For smooth Japan-U.S. trade, Artemus: ISF, AMS, AES, & Japan AFR Filing Software offers streamlined filing for Importer Security Filing (ISF), Automated Manifest System (AMS), and Automated Export System (AES), ensuring compliance and efficient exports.
Table Of Contents
Japan’s trade landscape in 2024 reflects a dynamic shift in global commerce. As the world economy adapts to new challenges and opportunities, Japan’s import and export activities play a crucial role in shaping its economic future.
In 2024, Japan’s trade dynamics are heavily influenced by its leading export sectors and fluctuating import demands. Japanese exports, which include vehicles, machinery, electronics, and refined oil products, have shown resilience and steady growth, especially in the automobile and tech sectors.
The country continues to meet demand in key markets like the United States, China, and the European Union, maintaining these as top export destinations.
Despite a persistent trade deficit, Japan’s exports increased by 5.6% in recent months, marking a consecutive streak of growth, although still slightly under expected forecasts.
On the import side, Japan is seeing a more modest growth trend, with energy imports—particularly liquefied natural gas (LNG) and crude oil—remaining essential due to limited domestic energy resources. These imports are vital to power Japan’s industries and sustain its high energy needs.
As Japan continues to strengthen its global trade ties, its ability to adapt to changing conditions will be essential to sustaining its competitive position in the international market.
Related: What Is AMS In Shipping Industry? A Beginner’s Guide

Japan’s trade relations in 2023 were influenced by shifting global dynamics and geopolitical factors. Despite challenges, the country’s strategic trade partnerships and new agreements played a key role in maintaining its economic stability.
In 2023, Japan’s trade landscape showed distinct shifts in both imports and exports due to several global and regional factors. Japan’s exports maintained steady growth, particularly in high-value sectors like machinery, electronics, and vehicles, which continue to be the backbone of its export economy.
The United States, China, and the European Union were among Japan’s main trading partners. However, trade with China faced hurdles, notably with the ban on Japanese seafood following the release of treated water from the Fukushima plant.
This seafood embargo hit Japan’s fishing industry hard, reducing exports of scallops and other products by significant percentages, though agricultural and other food exports, like sauces and seasonings, saw an increase in regions like Hong Kong and the United States.
For imports, Japan continued to rely heavily on fossil fuels, particularly from countries like Australia and the Middle East, due to limited domestic energy resources. The weaker yen made imports more expensive, impacting the trade balance, which has been in deficit for several consecutive years.
The government has been actively seeking to expand export markets and promote local industries with a goal of reaching ¥2 trillion in exports by 2025.
Japan’s strategic trade relationships and adaptability in 2023 ensured its continued presence as a major global trade player, despite global challenges.

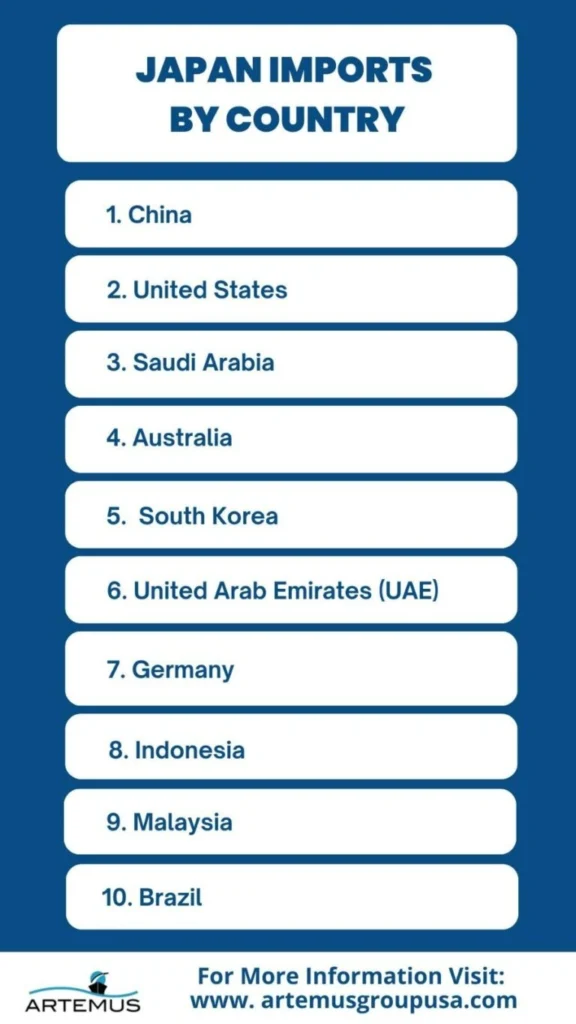
Japan’s imports are spread across many countries, with each providing essential resources that contribute to the country’s diverse industrial and technological sectors.
These countries play a significant role in ensuring a steady supply of goods and raw materials needed for Japan’s economic growth.
China is Japan’s largest import partner. The country supplies a range of goods, including electronics, machinery, textiles, and raw materials, such as semiconductors and components critical to Japan’s technological and industrial sectors.
The United States is Japan’s second-largest import partner. Key imports include agricultural products like soybeans, meat, and dairy, as well as machinery, aircraft, and chemicals that are essential for Japan’s automotive and manufacturing industries.
Saudi Arabia is a key energy supplier to Japan, providing significant amounts of crude oil and liquefied natural gas (LNG). These imports are vital for Japan’s energy consumption due to its limited domestic resources.
Australia is a major supplier of raw materials to Japan, particularly coal, iron ore, and natural gas. These resources are crucial to Japan’s industrial and manufacturing sectors.
South Korea is an important supplier of electronic components, including semiconductors and displays. Japan also imports vehicles and petrochemical products from South Korea.
The United Arab Emirates supplies crude oil to Japan, along with metals and chemicals. The UAE’s role in Japan’s energy supply chain is particularly significant.
Germany is a key partner in Japan’s import of high-tech machinery, pharmaceuticals, and automotive parts. The industrial and technology sectors in both countries are highly integrated.
Japan imports a variety of products from Indonesia, including coal, palm oil, liquefied natural gas, and agricultural products such as rubber and coffee.
Malaysia is a notable supplier of electronic components, semiconductors, and raw materials like crude oil, rubber, and palm oil to Japan.
Brazil is a key supplier of agricultural products like soybeans, coffee, and beef, as well as iron ore and other minerals, which are vital to Japan’s manufacturing industry.
These countries are integral to Japan’s import sector, ensuring the steady supply of critical goods that fuel the country’s economic engine. Import Regulations and Standards in Japan


Japan’s exports are crucial to its economic success, with the country sending a wide range of products to different regions. Japan’s trade relationships are shaped by its technological expertise, high-quality manufacturing, and strong global demand for its goods.
The United States is Japan’s largest export partner. Japan exports a variety of products to the U.S., including automobiles, auto parts, machinery, electronics, and precision instruments. The automotive sector plays a significant role, with companies like Toyota, Honda, and Nissan leading exports.
China is another major destination for Japanese exports, particularly in electronics, machinery, and automotive parts. Japan also exports optical and medical devices, industrial equipment, and semiconductors to China, which is crucial for its manufacturing and tech sectors.
The European Union remains an important market for Japan’s exports. Major exports include automobiles, industrial machinery, electronics, and chemicals. Japan’s high-tech and precision equipment is in demand across the EU, particularly in industries like automotive and electronics.
South Korea imports a wide range of products from Japan, including machinery, electrical equipment, and chemicals. Additionally, Japan exports vehicles and parts, as well as high-tech electronic components, crucial for South Korea’s own manufacturing sector.
Japan exports vehicles, machinery, and electrical appliances to Australia. The demand for high-quality industrial products, consumer goods, and automotive parts in Australia makes it one of Japan’s key export markets.
Taiwan is a significant destination for Japan’s high-tech products, especially semiconductors, machinery, and electrical equipment. Japan also exports vehicles and industrial machinery, crucial for Taiwan’s manufacturing and technology sectors.
Hong Kong is a vital trade hub for Japan, especially for re-exports to mainland China. Japan exports machinery, precision instruments, and electronics to Hong Kong, which serves as a gateway for these goods into China and other Asian markets.
Japan’s exports to Thailand include machinery, electronics, automotive parts, and chemicals. Japan’s high-quality machinery and electronics are widely used in Thailand’s manufacturing and automotive industries.
Japan exports a wide variety of products to Indonesia, including automobiles, machinery, electrical equipment, and steel. Indonesia’s growing industrial sector demands Japan’s high-quality technological products and equipment.
Vietnam is an emerging market for Japanese exports, particularly in electronics, machinery, and automobiles. Japan exports industrial machinery, electronic components, and consumer goods, which are vital to Vietnam’s rapidly expanding economy.
These countries play a key role in Japan’s export strategy, helping the nation maintain its strong position in global trade, particularly in technology, automotive, and industrial goods.
Related: What Is Import Compliance & Why It Matters?

Japan relies heavily on imports to meet its domestic demands across various sectors. Here are the key imports to Japan, along with relevant statistics:
Japan is one of the largest importers of energy products due to limited domestic resources. In 2023, Japan imported approximately $180 billion in fossil fuels, including liquefied natural gas (LNG), crude oil, and coal.
LNG is especially critical, making up a significant share due to the country’s dependency on imported gas for electricity and industrial energy needs World Integrated Trade Solution, JETRO.
Japan imports substantial quantities of electronic parts and machinery, including semiconductors, due to its advanced electronics and automotive sectors.
Imports of electrical machinery, including integrated circuits and digital components, exceeded $60 billion in recent years Trade.gov.
The country imports a significant amount of pharmaceutical products, valued at around $35 billion annually. This includes vaccines, diagnostic materials, and other medical equipment, a need amplified by Japan’s aging population JETRO.
While Japan is a leading exporter of automobiles, it also imports around $20 billion in automotive parts to support its extensive vehicle manufacturing industry. Imported parts often include electronics and specialized materials World Integrated Trade Solution, Trade.gov.
Due to limited arable land, Japan imports a wide range of agricultural goods, including grains, meat, and seafood. In 2022, agricultural imports were valued at about $50 billion, with the U.S. and the EU being major suppliers
Trade.gov.
Japan’s chemical industry is substantial, but certain raw materials and products are still imported. Chemical imports are valued at around $40 billion, covering everything from industrial chemicals to plastics JETRO.
Related: Japan AFR Filing (Advanced Filing Rules) For Compliance
Japan is one of the world’s top exporters, renowned for its advanced technological products and automotive industry. Here are some of Japan’s key export products:
Japan’s automotive industry is a global leader, with exports in vehicles and related parts contributing around $104 billion annually. Key exports include cars, motorcycles, and auto parts, with major buyers being the U.S., China, and several European countries.
Japan exports a substantial range of industrial machinery, including specialized production machinery and electric generators. Machinery accounts for a significant portion of exports, valued at approximately $180 billion annually, often to manufacturing-dependent nations.
Japan is a significant exporter of high-tech electronics, particularly semiconductor manufacturing equipment, which is essential for global tech production. Exports in this sector contribute over $30 billion annually, with the U.S., South Korea, and China as primary destinations.
Japan is known for precision optical and medical devices, such as cameras, lenses, and various diagnostic equipment. Exports in this category, valued around $25 billion, serve key markets like the U.S. and China.
Japan’s high-quality iron and steel products are crucial for industries worldwide, including construction and automotive. This sector brings in approximately $20 billion in exports each year, primarily serving Asian markets.
These products drive Japan’s trade partnerships, with the U.S. as its largest export market, followed closely by China and South Korea. Japan’s innovation-driven approach in these sectors maintains its competitive position in global markets.
Related: How To Import A Car From Japan To USA? A 7-Step Process
Japan’s trade is diverse, with the country importing and exporting a wide range of goods across various sectors. The country is known for its technological advancements, high-quality manufacturing, and industrial capabilities, all of which shape its major trade activities.
One of Japan’s most significant trade items in automobiles and automotive parts. Japan is a leading exporter of passenger cars, trucks, and automotive components, with global demand for Japanese vehicles due to their reputation for quality, innovation, and efficiency. Companies like Toyota, Honda, Nissan, and Subaru are at the forefront of Japan’s automotive exports.
Electronics and electrical equipment are another major trade for Japan. The country exports a wide range of products, including semiconductors, integrated circuits, televisions, cameras, and consumer electronics. Japan’s technological expertise in electronics and innovation in the field contribute to its leading position in global trade.
Japan is a key player in the global machinery and industrial equipment market. It exports precision machinery, industrial robots, machine tools, and construction equipment. These products are essential for manufacturing, construction, and high-tech industries worldwide.
Japan relies significantly on imports to meet its energy needs. It imports large quantities of crude oil, liquefied natural gas (LNG), and coal, which are essential for power generation and industrial activities. Despite its technological prowess, Japan has limited domestic energy resources, making energy imports vital for its economy.
To support its advanced manufacturing sectors, Japan imports significant quantities of raw materials and metals. Key imports include iron ore, copper, aluminum, and rare earth metals. These raw materials are crucial for industries like electronics, automotive, and manufacturing.
Japan is one of the world’s largest importers of food products, due to limited arable land for domestic agricultural production. It imports grains such as wheat, corn, and soybeans, as well as seafood, dairy, and fruits. These food products are vital to meet the needs of its population and food industries.
Japan is a significant player in the chemicals and pharmaceuticals trade, both as an importer and exporter. The country imports raw chemicals, organic compounds, and pharmaceuticals for use in its high-tech manufacturing sectors, while also exporting its own chemical products, medicines, and medical equipment globally.
Japan is a leading exporter of ships and boats, particularly large vessels like container ships, bulk carriers, and tankers. Japan’s shipbuilding industry is renowned for its high standards and cutting-edge technology, making it one of the world’s top exporters of these products.
Steel and metal products are also a major export for Japan. The country exports a wide range of metal products, including steel, copper, and aluminum, which are used in various industries such as construction, automotive, and electronics.
Japan is known for its high-quality optical and medical instruments, including cameras, microscopes, and medical equipment. These instruments are highly valued for their precision and innovation and are in demand across global healthcare and industrial sectors.
Japan’s trade is marked by a strong export sector, particularly in technology, automotive, and industrial goods. Simultaneously, the country’s reliance on imports, especially for energy, raw materials, and food, shapes its overall trade structure.
Related: 5 Types Of ISF Penalty & Fines To Know To Avoid Losses
Technology plays an integral role in Japan’s trade, influencing both the country’s exports and imports. As one of the world’s leaders in technological innovation, Japan leverages its expertise to maintain a competitive edge in global markets.
Japan’s advancements in technology have positioned it as a leading exporter of high-tech goods. Products like semiconductors, robotics, precision instruments, and electronics are at the forefront of Japan’s exports. Major companies such as Sony, Panasonic, and Toyota drive Japan’s dominance in these markets, with high demand worldwide for products known for their innovation and quality.
While Japan is a global leader in technology, it also depends on imports of key components to sustain its industries. Semiconductors, rare earth metals, and raw materials for electronics are crucial imports for Japan. These materials are essential for producing the high-tech goods that Japan exports and for supporting its growing industries like electric vehicles and robotics.
Technology has revolutionized Japan’s manufacturing sector, allowing for high efficiency and precision. The use of advanced robotics, automation, and AI in manufacturing processes has enhanced Japan’s competitiveness, especially in automotive and electronics industries.
This innovation supports the country’s export capabilities, ensuring that Japan remains a leader in high-quality products globally.
Technology continues to drive Japan’s economic growth, playing a critical role in the development of exportable goods and the efficiency of imports. By relying on cutting-edge innovations, Japan strengthens its position as a global trade powerhouse.
Related: Late ISF Filing: What To Do If Missed The Deadline?
Japan’s trade policies play a crucial role in shaping its import and export landscape, fostering economic growth while maintaining global competitiveness.
Japan actively participates in free trade agreements like the CPTPP and Japan-EU Economic Partnership Agreement, reducing tariffs and expanding market access for exports, while allowing cheaper imports.
Japan has low tariffs on industrial goods, promoting exports, but maintains higher tariffs on agricultural products, which protects local farmers and impacts food imports.
Trade policies support technological innovation, ensuring Japan remains competitive in high-tech exports while relying on imports of raw materials and advanced components.
Government initiatives and organizations like JETRO help promote Japanese exports, especially in sectors like electronics, machinery, and automotive, enhancing global demand.
Japan shields domestic industries through protectionist measures, particularly in agriculture, limiting imports but safeguarding local industries.
In summary, Japan’s trade policies balance free trade with strategic protectionism to support its key industries, encourage exports, and regulate imports effectively.
Related: AMS Fee In Shipping: Overview & 5 Key Considerations
Japan’s import and export sectors face several challenges despite the country’s strong position in global trade. These challenges impact both the flow of goods into the country and Japan’s ability to expand its exports.
Japan’s aging population is a significant challenge, affecting labor availability and productivity in both manufacturing and logistics sectors. As the workforce shrinks, there are concerns over maintaining efficient production and export capabilities.
Japan is heavily reliant on a few countries for both imports and exports. Its dependence on China and the United States for trade exposes Japan to risks such as trade disruptions, tariffs, and geopolitical tensions, which can affect the stability of its trade flows.
Japan is highly susceptible to natural disasters, including earthquakes, tsunamis, and typhoons. These events can disrupt manufacturing processes, damage infrastructure, and delay shipments, impacting both imports and exports.
Japan imports a large portion of its energy resources, including oil, natural gas, and coal. Global energy price fluctuations or supply disruptions can severely affect Japan’s economy, raising costs for industrial production and increasing reliance on foreign energy sources.
While Japan is known for its technological advancements, strict environmental regulations can make it more challenging to balance both domestic production and imports. There is also the challenge of ensuring that its exports meet international environmental standards, particularly in sectors like electronics and automobiles.
In conclusion, Japan’s import and export sectors face challenges related to demographic changes, trade dependencies, natural disasters, energy security, and environmental regulations, which could impact future growth and trade stability.
Related: AMS Filing Penalty Cost: Most Common Pitfalls & Solutions
Japan’s trade plays a central role in the Asia-Pacific region, influencing economic trends and fostering deeper economic integration among neighboring countries. As a key player in both regional and global trade, Japan’s policies and trade partnerships significantly impact the Asia-Pacific’s economic landscape.
Japan actively participates in major regional trade agreements like the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
These agreements aim to reduce trade barriers, enhance market access, and promote regional economic cooperation, strengthening Japan’s trade relations with key Asia-Pacific economies such as China, South Korea, and Southeast Asian nations.
Japan’s trade relationships with key regional partners, particularly the United States, Australia, and China, have significant geopolitical and economic implications.
These countries are essential for Japan’s trade, investment flows, and technological exchanges. Japan’s participation in multilateral trade negotiations and alliances enhances stability and promotes free trade in the region.
China is one of Japan’s largest trading partners, and the flow of goods between the two countries plays a crucial role in the Asia-Pacific trade network.
However, Japan’s reliance on China presents risks due to ongoing geopolitical tensions and trade disputes. To mitigate these risks, Japan has been diversifying its trade partnerships within the region.
Japan increasingly focuses on expanding its export markets in emerging Asia-Pacific countries, including those in Southeast Asia.
These nations, with growing consumer markets and expanding industries, present significant opportunities for Japan in sectors such as electronics, automobiles, and industrial machinery.
Japan’s technological expertise in areas like robotics, electronics, and automotive manufacturing has made it a key exporter of high-tech products in the Asia-Pacific. This technological exchange boosts Japan’s trade with regional partners while also making Japan a center for innovation in the region.
In conclusion, Japan’s trade policies and relationships within the Asia-Pacific region are critical to maintaining its economic strength and global influence. Through strategic trade agreements, partnerships, and technological innovation, Japan plays a key role in shaping the region’s economic future.
Related: Merchandise Processing Fee (MPF): A Complete Guide
Artemus specializes in Japan AFR filing services, helping businesses comply with Japan’s Advance Filing Requirement for imports.
This requirement mandates that specific shipment information be submitted to Japanese customs before goods arrive. Artemus ensures that all necessary data is accurately filed to prevent customs delays and penalties.
The team at Artemus handles the preparation and submission of detailed documentation, such as product descriptions, HS codes, and shipping information. This service streamlines the process, ensuring timely clearance at Japan’s ports and reducing the risk of costly hold-ups.
By relying on Artemus for AFR filing, businesses can navigate Japan’s import regulations efficiently. The service not only ensures compliance but also supports smoother trade operations, enhancing the overall import process for companies looking to do business in Japan.
Related: ISF Filing Requirements: A Step-By-Step Guide
Japan’s major imports include mineral fuels, machinery, electrical equipment, and chemicals. Its major exports consist of automobiles, machinery, electrical machinery, and optical/medical instruments.
Five major imports in Japan are crude oil, petroleum products, electrical machinery, chemicals, and foodstuffs.
Japan’s chief exports include automobiles, machinery, electrical machinery, optical and medical instruments, and steel products.
The United States is Japan’s top export destination, followed by China and other countries.
Japan is famous for its technology, automotive industry, culture (including anime and traditional arts), and its rich history and food, particularly sushi.
Japan’s main source of income comes from its high-tech manufacturing industry, including automobiles, electronics, and machinery.
Japan imports a variety of goods from India, including gems, textiles, chemicals, and agricultural products like spices.
People move to Japan for various reasons, including job opportunities, educational pursuits, and cultural experiences, as well as the country’s advanced healthcare and high standard of living.
Japan imports soybeans, wheat, meat, dairy products, and fruits (such as bananas and apples).
China is Japan’s biggest trading partner, followed by the United States and South Korea.
Japan’s economy is strong due to its advanced technology, efficient manufacturing, high-quality exports, and strong industrial sectors like automobiles and electronics.
Japan imports most of its raw materials, such as crude oil, coal, iron ore, copper, and natural gas, to support its manufacturing industries.

In conclusion, Japan’s imports and exports are essential to its economic strength. The country relies on imports for raw materials and energy, while its exports, particularly in technology and automobiles, highlight its manufacturing expertise.
Trade partnerships with countries like the United States, China, and the EU are crucial for Japan’s global economic influence. These relationships ensure Japan’s position in the international market and contribute to global supply chains.
Japan’s ability to manage both imports and exports effectively ensures its continued growth and resilience in a dynamic global economy. With ongoing innovation, Japan remains a key player in international trade.
Related: Which Party Issues The Export Declaration Document?


International trade between the United States and Switzerland highlights the strong economic relationship between the two nations. With its highly

Cold Nordic waters, advanced engineering, and a strong maritime economy make Norway a powerful exporter despite its size. Many of

Trade between the United States and Canada is one of the largest bilateral trading relationships in the world. Understanding what
Get In Touch
Artemus’ Software Solutions for ISF, AMS, Japan AFR, eManifest Canada, & Panama B2B filings.