
What Does Switzerland Export To The US? A Detailed Guide
Switzerland plays a vital role in U.S. trade, supplying a wide range of high-value and specialized products. From pharmaceuticals and


When navigating the world of international shipping, understanding the roles of a Customs Broker vs. Freight Forwarder is essential for smooth and compliant trade operations. While both professionals play vital roles in the logistics chain, their responsibilities differ significantly.
In this guide, we’ll explore the five key differences between customs brokers and freight forwarders, helping you determine which service best fits your import/export needs. Customs brokers focus on ensuring shipments comply with customs regulations, while freight forwarders manage the entire logistics process, from coordinating transport to handling storage.
For companies & individuals looking to streamline their compliance and logistics processes, Artemus offers robust customs compliance software solutions, including ISF and AMS filings, that can be either self-filed or managed with Artemus’s support.
With specialized customs brokers software and freight forwarders software, Artemus enables easy filing for AMS, ISF, and AES, simplifying multiple filings and ensuring seamless trade compliance.
Table Of Contents
A customs broker is a licensed professional who specializes in ensuring that goods being imported or exported comply with all relevant customs regulations. They play a vital role in international trade, acting as the intermediary between importers/exporters and government authorities.
Their primary function is to facilitate the smooth movement of goods across borders by handling the complex documentation and legal requirements necessary for customs clearance. With deep knowledge of tariffs, taxes, and specific import/export laws, customs brokers ensure that shipments meet compliance standards, avoiding costly penalties and delays.
The roles and responsibilities of a customs broker are multifaceted. They prepare and submit essential documents, including import declarations and tariff classifications, to Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and other regulatory bodies. Customs brokers also assess duties, taxes, and fees applicable to shipments, ensuring accurate payments to avoid future discrepancies.
In addition, they advise clients on compliance issues, such as product restrictions, labeling, and country-specific regulations, helping businesses avoid fines and legal complications associated with non-compliance.
Related: Can A Customs Broker Be The Importer Of Record Legally?
A freight forwarder is a company or individual that specializes in managing the logistics of shipping goods internationally. Acting as a crucial link between shippers and transportation services, freight forwarders coordinate the end-to-end journey of goods, whether by sea, air, rail, or road, ensuring that shipments reach their destination efficiently and securely.
They play a strategic role in supply chain management, utilizing their expertise to optimize routes, consolidate shipments, and select the most cost-effective and reliable carriers for their clients.
The primary responsibilities of a freight forwarder include arranging transportation, handling warehousing, and preparing all necessary shipping documentation. Freight forwarders manage the intricate logistics of cross-border shipments, coordinating schedules and routes while handling documentation like bills of lading, export licenses, and certificates of origin.
Additionally, they arrange for cargo insurance, providing clients with added security and peace of mind. Freight forwarders also consolidate multiple shipments into a single container when needed, reducing costs and improving shipping efficiency, particularly for smaller shipments.
Related: Customs Broker Exam (CBLE): A Comprehensive 2024 Overview
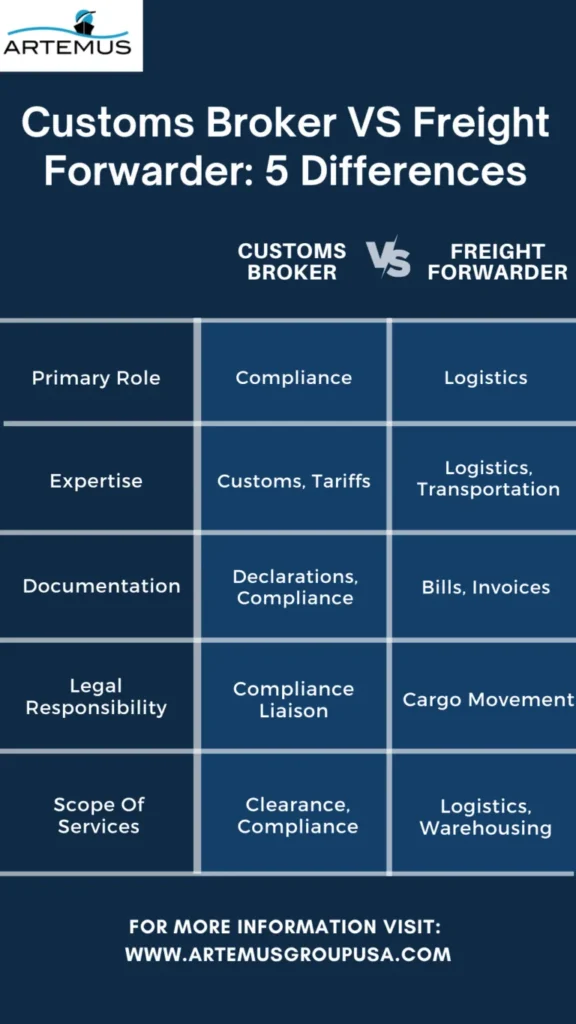
Let’s explore five significant distinctions that set customs brokers apart from freight forwarders and clarify their respective contributions to the supply chain and trade facilitation.
Customs Broker: A customs broker primarily focuses on navigating the legal and regulatory aspects of international trade, ensuring compliance with customs laws and regulations.
Freight Forwarder: A freight forwarder, on the other hand, specializes in logistics and transportation, managing the movement of goods from the point of origin to the destination.
Customs Broker: Customs brokers are experts in customs procedures, import and export documentation, and tariff classifications. They guarantee that shipments are in full compliance with all legal standards.
Freight Forwarder: Freight forwarders excel in managing the logistics of shipping, negotiating with carriers, arranging transportation, and optimizing routes for cost efficiency.
Customs Broker: Customs brokers specialize in handling extensive paperwork, including customs declarations, duty and tax calculations, and compliance with import/export regulations.
Freight Forwarder: Freight forwarders manage documentation related to shipping and transportation, such as bills of lading, packing lists, and freight invoices.
Customs Broker: Customs brokers bear a legal responsibility to ensure that all customs requirements are met, and they act as a direct liaison between clients and customs authorities.
Freight Forwarder: Freight forwarders are responsible for the safe and timely movement of cargo but typically do not have the same level of legal responsibility as customs brokers in terms of customs compliance.
Customs Broker: Customs brokers often offer specialized services related to customs clearance, classification, and compliance, and they frequently work on behalf of importers and exporters.
Freight Forwarder: Freight forwarders provide a more comprehensive range of services, including cargo booking, tracking, consolidation, warehousing, and managing the entire logistics process, making them essential partners for the entire shipping journey.
Related: What Are The Likely Customs Broker Exam Pass Rate For 2024?
Customs brokers and freight forwarders are integral components of the international trade and shipping process, and their roles often complement each other in several ways.
Customs brokers bring their in-depth knowledge of import/export regulations, customs procedures, and documentation requirements. They ensure that shipments comply with all legal standards.
Freight forwarders, on the other hand, excel in transportation logistics and have strong relationships with carriers and shipping lines. Their collaboration ensures that the entire process, from compliance to transportation, runs smoothly.
Customs brokers handle the extensive customs paperwork, ensuring that all necessary documents are complete and accurate.
They work closely with freight forwarders to provide them with the required documentation for the transportation phase. This seamless exchange of information streamlines the process and minimizes the risk of delays or errors.
Customs brokers act as liaisons between clients and customs authorities, while freight forwarders manage the physical movement of goods. Effective communication and coordination between the two are essential for ensuring that shipments arrive on time and in compliance with regulations.
Customs brokers help identify and mitigate potential compliance risks, such as incorrect tariff classifications or incomplete documentation, reducing the chances of costly customs delays or penalties.
Freight forwarders contribute to risk management by optimizing transportation routes, ensuring cargo security, and providing insurance options to protect against unforeseen circumstances.
Collaboratively, customs brokers and freight forwarders offer end-to-end services that cover the entire logistics chain. This includes customs clearance, transportation planning, cargo tracking, warehousing, and even final delivery to the destination.
This comprehensive approach provides clients with a one-stop solution for their international trade and shipping needs.
Related: Custom Broker Fees Explained: The Figures You Need To Know
When it comes to managing international shipments, both customs brokers and freight forwarders play critical roles in ensuring goods move smoothly across borders. But these professionals serve different purposes, and choosing the right one depends on your shipping needs.
Choose a customs broker if:
Choose a freight forwarder if:
Yes, many businesses use both. A customs broker handles the specifics of customs clearance, while a freight forwarder manages the overall logistics. Together, they ensure a smooth and efficient shipping experience, from origin to destination, while minimizing regulatory risks.
For seamless international shipping, using a customs broker, freight forwarder, or both depends on the scope of your needs. If compliance is your main concern, a customs broker is essential. If you need holistic logistics support, consider a freight forwarder or both professionals working in tandem.
Related: Customs Bond Renewal: All Facts You Need To Know
Yes, a freight forwarder can act as the Exporter of Record (EOR) in certain circumstances, but it depends on the specific needs of the export and the legal requirements of the destination country.
Acting as the Exporter of Record means the freight forwarder assumes responsibility for ensuring the shipment meets all regulatory requirements, including accurate documentation, compliance with export laws, and paying any necessary export duties and taxes.
By taking on this role, the freight forwarder manages the risks associated with customs compliance, especially for companies without an established presence in the destination country.
However, not all freight forwarders offer EOR services, as it involves additional liability and specialized knowledge of international trade regulations. When they do, this service is especially valuable to businesses without in-house expertise or a legal entity in the export destination.
Artemus offers advanced Customs Broker Software and Freight Forwarders Software specifically designed to streamline customs compliance processes for international shipments. With a focus on accuracy, efficiency, and regulatory adherence, Artemus software simplifies the management of critical filings such as AMS, ISF, and AES.
For customs brokers, this software provides powerful tools to handle complex documentation and customs regulations, ensuring smooth and compliant customs clearance while reducing the risk of costly delays and penalties.
For freight forwarders, Artemus software offers an all-in-one solution to manage logistics and customs documentation seamlessly, from origin to destination.
Typically, you’ll need to provide invoices, bills of lading, packing lists, and any relevant permits or licenses for your shipment.
Some freight forwarders offer customs clearance services, but this is not their primary role. They can collaborate with customs brokers for this aspect.
Research reputable freight forwarders with a strong track record, consider their industry specialization and evaluate their network of carriers and logistics capabilities.
No, a freight broker arranges transportation, while a customs broker handles import compliance and customs clearance.
A freight broker arranges transport between carriers and shippers, while a forwarder manages end-to-end logistics, including storage and documentation.
A customs broker facilitates import compliance by handling customs documentation, tariffs, and regulations.
Another name for a freight forwarder is “forwarding agent” or simply “forwarder.”
Freight forwarding involves managing the transportation of goods, while customs pertains to the clearance of goods through a country’s border.
Yes, freight forwarders often work with brokers to arrange transportation and customs clearance.
Choose a freight forwarder to streamline logistics, ensure compliance, and manage the complexities of international shipping.
Businesses shipping goods internationally often need a freight forwarder for efficient logistics and compliance.
Importers, exporters, and businesses of all sizes use freight forwarders to manage international shipping.
To become a customs broker in the US, individuals must pass the CBP broker exam and meet licensing requirements.
Importers use customs brokers to navigate customs regulations and ensure their goods clear customs smoothly.
The job of a customs broker is to assist importers with compliance, documentation, and duty payments for customs clearance

In the dynamic world of international trade, understanding the differences between customs brokers and freight forwarders is crucial for businesses seeking seamless global operations. We’ve explored five key distinctions that set these roles apart: legal authority and responsibilities, scope of services, interaction with government agencies, liability and legal accountability, and collaboration.
Customs brokers are the experts when it comes to customs compliance, ensuring that your shipments meet the strict regulatory requirements. In contrast, freight forwarders specialize in logistics and transportation, offering end-to-end solutions for moving goods efficiently.
By grasping these differences, businesses can make informed decisions, knowing when to engage the services of customs brokers or freight forwarders, and often, recognizing the advantages of leveraging both to maximize the efficiency of their international trade endeavors.
Related: What Is A Customs Bond? A Guide For Importers & Others


Switzerland plays a vital role in U.S. trade, supplying a wide range of high-value and specialized products. From pharmaceuticals and

In 2026, the US-Europe trade relationship continues to power global commerce, driven by exports of energy, advanced machinery, and pharmaceuticals

The economic partnership between the United States and Norway is a sophisticated and evolving pillar of transatlantic commerce. U.S. exports
Get In Touch
Artemus’ Software Solutions for ISF, AMS, Japan AFR, eManifest Canada, & Panama B2B filings.