
What Does Norway Export To The US? Key Products & Trade Data
Cold Nordic waters, advanced engineering, and a strong maritime economy make Norway a powerful exporter despite its size. Many of


In the dynamic world of supply chain management, understanding the nuances of inbound and outbound logistics is crucial for operational efficiency and business success. Inbound logistics refers to the process of receiving, handling, and storing raw materials or goods from suppliers, while outbound logistics involves the distribution and delivery of finished products to customers.
In 2026, the logistics landscape continues to evolve, emphasizing automation, real-time tracking, and regulatory compliance. This is where Artemus steps in! As a leading provider of software solutions for Customs Brokers, NVOCCs, and Freight Forwarders, Artemus simplifies ISF (Importer Security Filing), AMS (Automated Manifest System), and AES (Automated Export System) filings.
With advanced features for error reduction, automated data submission, and real-time tracking, Artemus ensures your logistics processes are efficient, compliant, and hassle-free.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the key differences, processes, and best practices of inbound and outbound logistics, highlighting how advanced solutions like Artemus can streamline global trade operations.
Table Of Contents
Inbound logistics refers to the process of managing and overseeing the transportation, storage, and delivery of goods and materials coming into a business.
It focuses on the supply side of the supply and demand equation and includes the steps required to order, receive, transport, store, and manage incoming raw materials, components, or products from suppliers.
It encompasses the coordination of sourcing and procurement, purchasing, transportation mode selection, receiving, material handling, putaway, warehousing, and inventory management to ensure goods arrive at the right place, at the right time, and in the right condition.
Inbound logistics also involves tracking shipments, expediting delayed materials, distributing supplies internally within the organization, and managing documentation related to incoming orders.
In some cases, it includes reverse logistics activities such as returns, repairs, recycling, or refurbishment of materials.
This process is critical for maintaining efficient production schedules, reducing costs, and ensuring product quality. Efficient inbound logistics supports better supplier relationships, minimizes delays, reduces transportation and storage expenses, and improves inventory accuracy.
Depending on the industry, type of goods, and buyer-seller relationship, companies may manage inbound logistics internally or outsource it to third-party logistics providers.

Related: Top 10 Ports In The USA: The Busiest Hubs Driving US Trade
Outbound logistics refers to the process of managing the storage, transportation, and distribution of finished goods from a business to its customers or end users.
It focuses on the demand side of the supply and demand equation and covers the movement of products from warehouses or production facilities to their final destination. This process includes order fulfillment, packing, shipping, delivery, and customer service related to delivery.
Outbound logistics involves activities such as warehouse and storage management, inventory management, order processing, packaging, transportation, and shipping to ensure that products are delivered accurately, on time, and in optimal condition.
It also includes managing distribution channels, whether products are sold directly to customers or through intermediaries such as wholesalers, retailers, or dealers. For many businesses, outbound logistics overlaps with inbound logistics in warehouse operations, but it specifically focuses on handling outgoing finished goods.
The goal of outbound logistics is to efficiently move products through the supply chain while meeting customer expectations and minimizing costs.
Effective outbound logistics strategies emphasize selecting appropriate transportation modes, optimizing delivery routes, managing last mile delivery, and leveraging technology such as inventory management systems, route optimization software, and real time tracking tools.
These efforts help improve delivery speed, accuracy, visibility, and product quality while reducing losses, delays, and inefficiencies.
Related: How To Get Import And Export License In USA: Quick Overview
In supply chain management, inbound logistics and outbound logistics are two essential components that support the movement of goods across the broader supply chain. While logistics is a key function, supply chain management (SCM) oversees the entire network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, service providers, and customers.
Inbound logistics in supply chain management focuses on the movement, storage, and delivery of raw materials, components, and goods coming into a business from suppliers. It includes sourcing, procurement, supplier coordination, transportation, receiving, inspection, storage, and inventory management.
The objective is to ensure materials arrive on time, in the correct quantity, and in acceptable condition to support production and operational continuity. Inbound logistics also plays a role in supplier collaboration, quality control, risk management, and cost reduction through accurate forecasting and efficient ordering systems.
Outbound logistics deals with the distribution of finished products from the business to customers, retailers, wholesalers, or distribution partners. It includes order processing, packaging, warehousing of finished goods, transportation planning, shipping, and last-mile delivery.
The goal is to move products out of the business efficiently and accurately while meeting delivery timelines, service-level agreements, and customer expectations. Outbound logistics often involves close coordination with logistics providers on packaging standards, scheduling, route optimization, and delivery performance.
Together, inbound and outbound logistics form the operational backbone of supply chain management by controlling the flow of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption.
Effective logistics supports supply chain partnerships through shared information, coordinated decision-making, and resource alignment between suppliers, logistics providers, and customers.
Optimizing both inbound and outbound logistics reduces costs, minimizes risk such as loss or damage during transit or storage, improves operational efficiency, and enhances overall customer satisfaction.

Related: 10 Supply Chain Best Practices In Shipping: A 2025 Guide
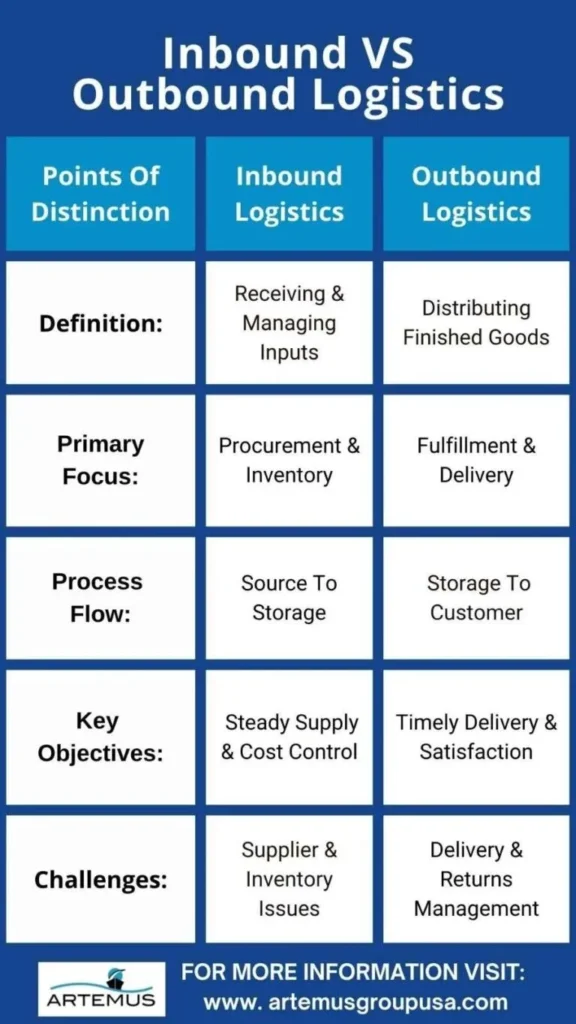
Inbound and outbound logistics are critical components of supply chain management, but they focus on different stages of the product journey. Understanding their key differences is essential for optimizing operations and ensuring efficient supply chain flow.
In summary, while inbound logistics ensures the smooth inflow of materials for production, outbound logistics focuses on efficiently delivering finished goods to customers. Both are vital for a streamlined supply chain and achieving overall business efficiency.
Related: What Is Global Trade Management? A Complete 2025 Guide
Inbound logistics involves the systematic process of managing the flow of raw materials, components, and goods from suppliers to a business’s production or storage facilities.
A well-structured inbound logistics process ensures efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and timely availability of materials. Here’s an overview of the key steps involved:
The process begins with identifying and selecting reliable suppliers who can provide quality materials. Procurement involves negotiating contracts, setting delivery terms, and placing orders for the required goods.
After procurement, transportation arrangements are made to move goods from the supplier to the business’s facility. This includes selecting suitable transportation modes (road, air, sea) and managing logistics for timely and cost-effective delivery.
Upon arrival, goods are inspected to ensure they meet quality standards and match the purchase order specifications. This step involves checking for damages, verifying quantities, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Once verified, goods are recorded and stored appropriately. Efficient inventory management ensures that materials are organized, accessible, and tracked accurately to avoid stockouts or overstocking.
Materials are stored in designated warehouse locations, with considerations for safety, accessibility, and storage conditions. Proper warehousing ensures efficient retrieval when needed for production.
Accurate documentation is essential for tracking inventory levels, shipment details, and supplier information. Digital systems help streamline data management, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
Maintaining strong relationships with suppliers helps in negotiating better terms, resolving issues promptly, and ensuring consistent supply. Regular communication and performance reviews are part of this process.
By optimizing each step of the inbound logistics process, businesses can reduce costs, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure the timely availability of materials for production or distribution.
Related: List Of 12 Largest Shipping Ports In The World
Outbound logistics involves managing the flow of finished products from a business to its customers. It ensures that products are efficiently stored, packaged, and transported for timely delivery.
A well-optimized outbound logistics process enhances customer satisfaction, reduces costs, and ensures seamless operations. Here’s an overview of the key steps involved:
The process begins with receiving and confirming customer orders. This includes verifying product availability, processing payment, and preparing order documentation to ensure accurate fulfillment.
Once an order is processed, the required products are picked from inventory. Effective inventory management ensures products are readily available, reducing delays and preventing stock discrepancies.
Products are then securely packaged to prevent damage during transportation. This step also involves labeling packages with essential information like addresses, tracking codes, and handling instructions.
Before dispatch, packaged products are organized and stored in the warehouse. Efficient warehousing ensures quick retrieval and reduces the chances of shipping errors.
This involves selecting the best transportation method (road, air, sea, or rail) and planning delivery routes for cost-effective and timely delivery. Real-time tracking systems help monitor the shipment’s progress.
The products are transported and delivered to the customer’s location. Ensuring prompt and accurate delivery is key to enhancing customer satisfaction and maintaining trust.
In case of returns or damaged goods, a reverse logistics process is initiated. This includes collecting the products, processing refunds or replacements, and restocking if applicable.
Accurate documentation, including invoices, delivery receipts, and tracking details, is maintained for transparency and record-keeping.
By streamlining each stage of the outbound logistics process, businesses can improve delivery speed, reduce costs, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Related: NVOCC Bond & OTI Bonds – Federal Maritime Commission
Inbound and outbound logistics are critical components of a smooth and efficient supply chain. Together, they ensure that raw materials reach production on time and finished products are delivered to customers quickly, accurately, and cost-effectively.
Inbound logistics strategy is vital for protecting production flow and controlling supply chain risk. By taking ownership of how goods move from suppliers to facilities, businesses gain greater predictability, visibility, and cost control. The following points highlight why a strong inbound strategy matters:
Outbound logistics strategy is essential for delivering value to customers and sustaining revenue growth. Once products are ready, efficient outbound execution determines how quickly and accurately orders reach the market. The key reasons the outbound strategy is so important include:

Related: Do Tariffs Affect Shipping Costs? Key Facts & Insights
Inbound and outbound logistics are critical components of supply chain management, but each comes with its own set of challenges that can impact efficiency, cost, and customer satisfaction. Addressing these challenges is key to ensuring a smooth and reliable supply chain.
Related: What Is Harbor Maintenance Fee (HMF)? A 2025 Guide
Optimizing inbound and outbound logistics is essential for efficient supply chain management, cost reduction, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Implementing best practices in both areas ensures smooth operations, minimizes delays, and boosts overall profitability.
In 2026, businesses must emphasize real-time visibility, automated decision-making, and strong collaboration with partners to stay competitive.
Related: Merchandise Processing Fee (MPF): A Complete Guide
Artemus offers advanced software solutions designed to simplify and streamline ISF, AMS, and AES filings for Customs Brokers, NVOCCs, and Freight Forwarders. Our platform ensures seamless compliance with U.S. Customs regulations, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in managing international shipments.
With features tailored for automated data submission, real-time tracking, and error reduction, Artemus empowers businesses to handle Importer Security Filings (ISF), Automated Manifest Systems (AMS), and Automated Export System (AES) filings with ease.
Whether you’re looking to optimize documentation processes, minimize delays, or ensure regulatory compliance, Artemus’s user-friendly software is built to support your operational needs. Gain control over your logistics, improve filing accuracy, and meet critical deadlines, making your customs processes faster and more reliable.
Related: 5 Must-Know Differences Between Supply Chain And Logistics
Inbound logistics focuses on the receipt and storage of goods, while outbound logistics involves the distribution of finished products to customers.
Inbound freight refers to the transportation of goods coming into a business, while outbound freight involves the shipment of goods from the business to customers.
In the value chain, inbound logistics includes activities like receiving, storing, and managing raw materials essential for production.
No, inbound logistics is part of upstream logistics, focusing on the flow of materials into the business. Downstream logistics refers to outbound processes.
Outbound logistics is also known as distribution logistics.
Outbound logistics services are the activities involved in storing, handling, transporting, and delivering finished products from a business to customers, retailers, or distributors. This includes order fulfillment, packaging, warehousing, transportation, last-mile delivery, and reverse logistics for returns or exchanges.
Forward logistics is another term for outbound logistics, involving the movement of products from production to the end customer.
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving products backward in the supply chain for returns, repairs, recycling, or disposal.
To calculate inbound logistics, sum up all costs associated with bringing goods into your business, including:
Formula: Inbound Logistics Cost = Transportation + Receiving/Handling + Storage/Warehousing + Duties/Taxes

Inbound and outbound logistics are the backbone of efficient supply chain management, ensuring that materials and products move seamlessly from suppliers to customers. While inbound logistics focuses on sourcing and receiving goods, outbound logistics is all about delivering finished products to the end consumer.
Mastering both processes is essential for reducing costs, improving efficiency, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Related: Understanding Roll-On/Roll-Off Ships: A Complete Guide


Cold Nordic waters, advanced engineering, and a strong maritime economy make Norway a powerful exporter despite its size. Many of

Trade between the United States and Canada is one of the largest bilateral trading relationships in the world. Understanding what

Switzerland plays a vital role in U.S. trade, supplying a wide range of high-value and specialized products. From pharmaceuticals and
Get In Touch
Artemus’ Software Solutions for ISF, AMS, Japan AFR, eManifest Canada, & Panama B2B filings.